Intellectual Disability (ID) – Definition and Overview:
Intellectual Disability (ID) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior. It begins before the age of 18 and affects a person’s ability to learn, reason, solve problems, and function independently in daily life.
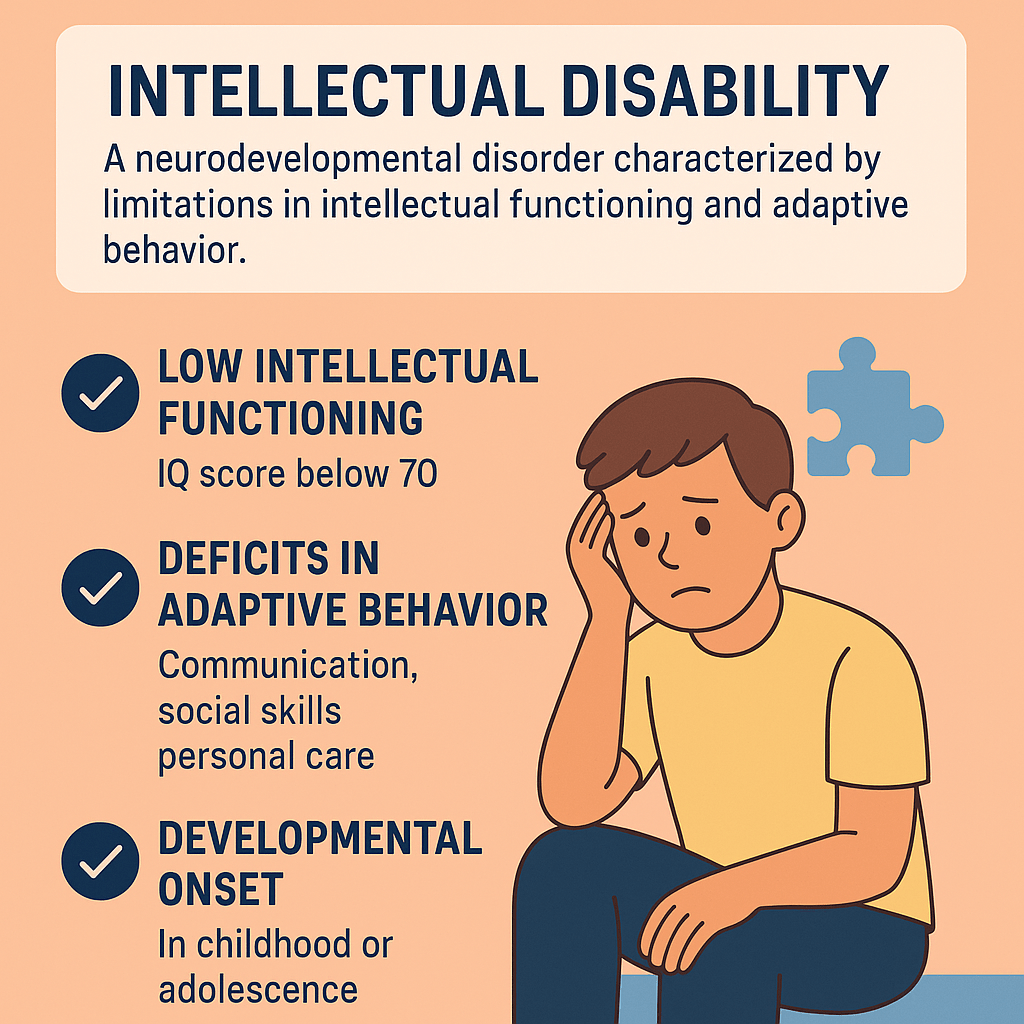
✅ Key Features of Intellectual Disability:
- Low Intellectual Functioning
- Typically measured by an IQ score below 70.
- Difficulties with reasoning, problem-solving, abstract thinking, and learning.
- Deficits in Adaptive Behavior
- Problems in practical life skills such as:
- Communication
- Social skills
- Personal care
- Home living
- Work and school functioning
- Problems in practical life skills such as:
- Developmental Onset
- Symptoms appear during childhood or adolescence, not later in life.
🧠 Causes of Intellectual Disability:
- Genetic conditions (e.g., Down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome)
- Prenatal exposure to alcohol, drugs, or infections
- Birth complications, such as oxygen deprivation
- Childhood diseases or brain injury
- Unknown causes (in many cases)
📊 Levels of Intellectual Disability:
| Level | IQ Range | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 50–69 | Can learn basic skills; may live independently with support. |
| Moderate | 35–49 | Needs regular support; limited communication and academic skills. |
| Severe | 20–34 | Significant support needed; limited verbal skills. |
| Profound | <20 | Constant care; minimal understanding or communication. |
🧩 Support and Treatment:
- Special education programs
- Speech and occupational therapy
- Social skills and life skills training
- Behavioral therapy
- Medical support for associated conditions
🛑 Important Note:
The term “mental retardation” was historically used but is now considered outdated and offensive. The preferred term globally is Intellectual Disability (ID)
Leave a comment