Here is a clear and concise summary of power shortages in India:
Summary of Power Shortages in India
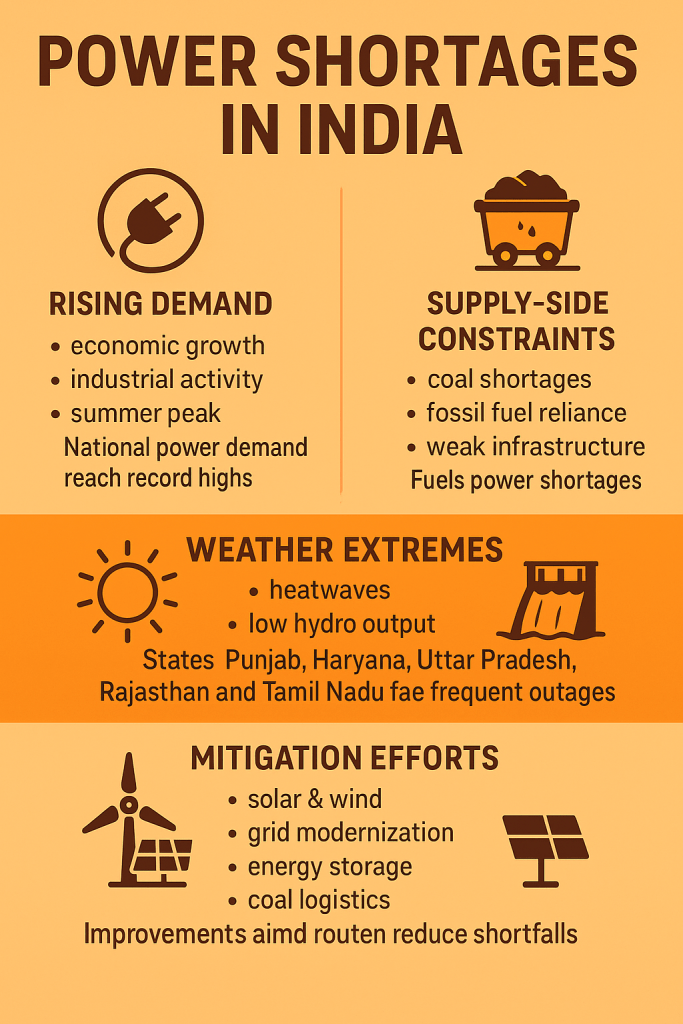
India faces periodic power shortages due to a combination of rising electricity demand and supply-side constraints. Rapid economic growth, increasing industrial activity, and higher residential consumption—especially during summer—have pushed national power demand to record highs.
On the supply side, key challenges include coal shortages, dependence on fossil-fuel plants, delays in renewable energy integration, and inadequate transmission infrastructure. Many thermal power plants operate with low coal stocks during peak seasons, causing load shedding in several states.
Weather extremes like heatwaves, weak monsoon periods, and low hydroelectric output further strain the grid. States such as Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu often face peak-hour shortages.
While India is expanding solar, wind, and battery storage capacity, the transition is gradual. Improvements in grid modernisation, energy storage, domestic coal logistics, and renewable integration are crucial to reducing recurring shortages.
Leave a comment