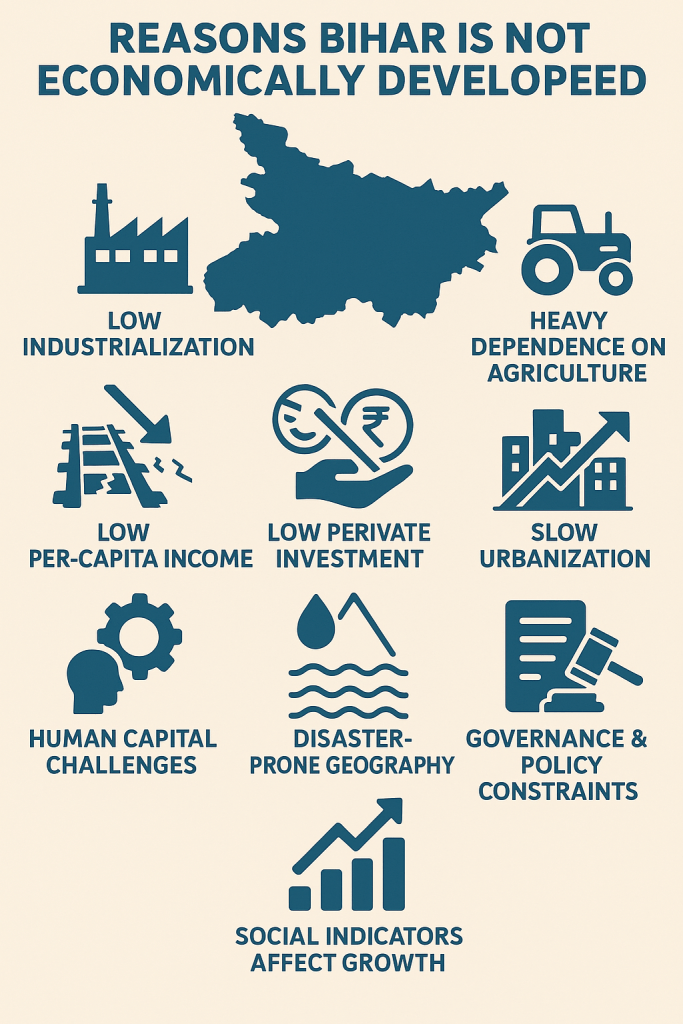
Here is an analytical summary of why Bihar is often viewed as not economically strong:—Analytical Summary: Bihar as Not Economically Developed
1. Low Industrialization
Bihar has very few large-scale industries. Manufacturing, IT, and processing sectors are limited. This restricts job creation and slows economic expansion.
2. Heavy Dependence on Agriculture A majority of the population depends on agriculture, which is low-income and vulnerable to floods, droughts, and poor irrigation. Lack of agro-industries reduces value addition.
3. Weak Infrastructure
Poor road connectivity in rural areas
Limited rail-based freight support Electricity supply challenges
These factors discourage investors from setting up industries.
4. Low Per-Capita Income Bihar consistently ranks among the lowest in per-capita income compared to other Indian states, reflecting limited earning opportunities.
5. Limited Private Investment Due to law-and-order concerns, land availability issues, and slow approval processes, private companies avoid long-term investments.
6. Slow Urbanization. Urbanization levels are among the lowest in India. Fewer cities means fewer economic hubs, industrial clusters, and service-sector opportunities.
7. Human Capital Challenges Though improvements are happening:Skill development levels are low High migration to other states for jobs This means Bihar loses potential workforce value.
8. Disaster-Prone Geography
Frequent floods in North Bihar and droughts in South Bihar disrupt agriculture, transport, and livelihoods, reducing economic stability.
9. Governance & Policy Constraints While governance has improved over time, historical issues such as:Bureaucratic delays
Slow reforms Limited fiscal capacity have slowed development momentum.
10. Social Indicators Affect Growth Challenges in health, schooling quality, and poverty directly impact productivity and long-term economic growth.—
Leave a comment