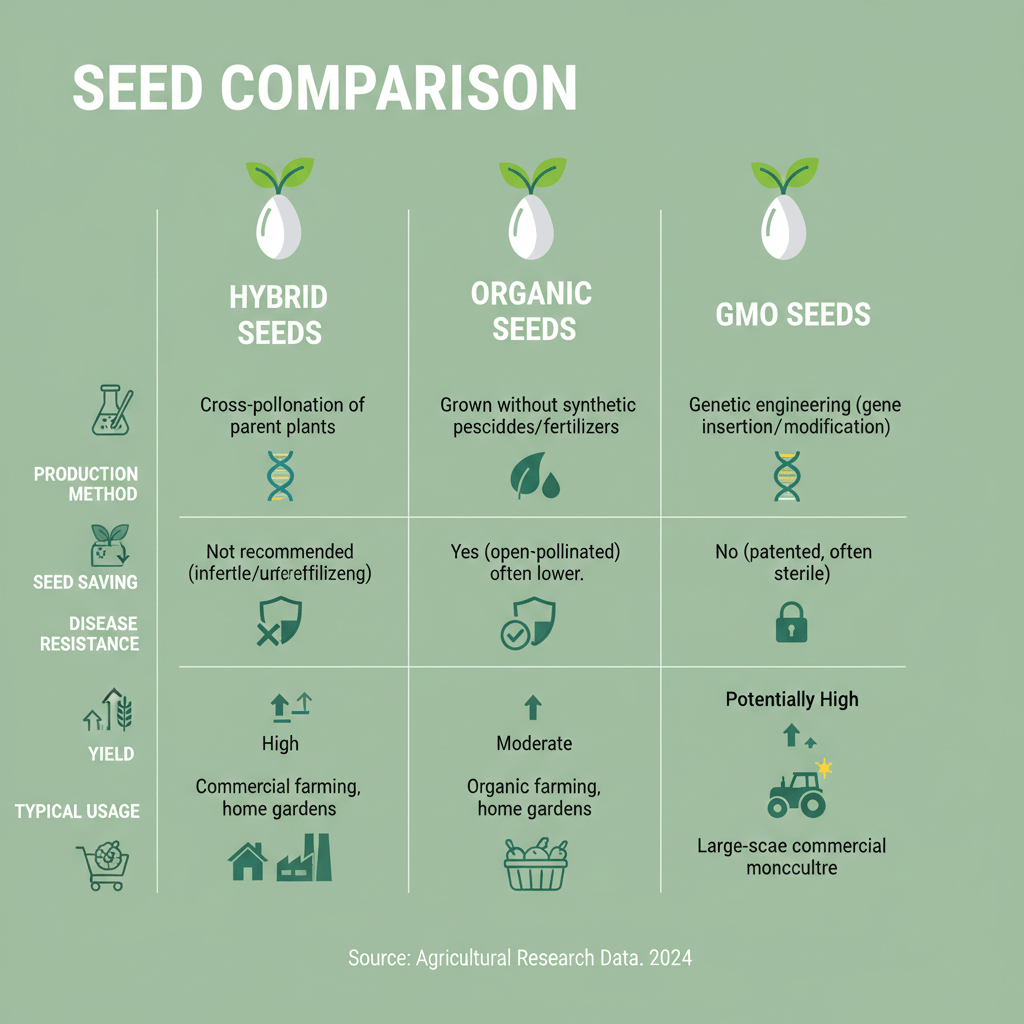
Hybrid, organic, and GMO seeds differ significantly in how they’re produced, their genetic stability, and their implications for farming and food quality.
Core Differences
Hybrid vs Organic Seeds
- Hybrid seeds are bred for specific traits like higher yield and disease resistance, but seeds from hybrid plants often don’t produce the same quality plants in the next generation.
- Organic seeds come from plants cultivated without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides and can be hybrid, non-hybrid, or heirloom—provided they meet organic standards.
- Organic/non-hybrid (heirloom) seeds allow for seed-saving and tend to have greater genetic and flavor diversity, while hybrid seeds are favored for consistent, predictable traits.
Hybrid vs GMO Seeds
- Hybrid seeds result from natural cross-pollination within a species, controlled by breeders to combine traits, not from genetic engineering.
- GMO seeds are genetically modified in the lab by inserting genes from other organisms, possibly other species, to confer traits like pest or herbicide resistance.
- Hybrids generally have good yield and disease resistance, whereas GMOs offer more targeted resistance but can raise environmental and health debates.
Organic vs GMO Seeds
- Organic seeds are inherently non-GMO, as GMO seeds are prohibited in organic certification.
- Organic seeds can be saved and produce consistent crops, while GMO seeds are regulated, primarily for commercial use, and are not available for home gardeners.
Summary Table
Hybrid seeds offer predictability and vigor, organic seeds support sustainability and seed saving, while GMO seeds deliver engineered traits for industrial agriculture—but with higher cost and controversy.
Sources
·
Leave a comment