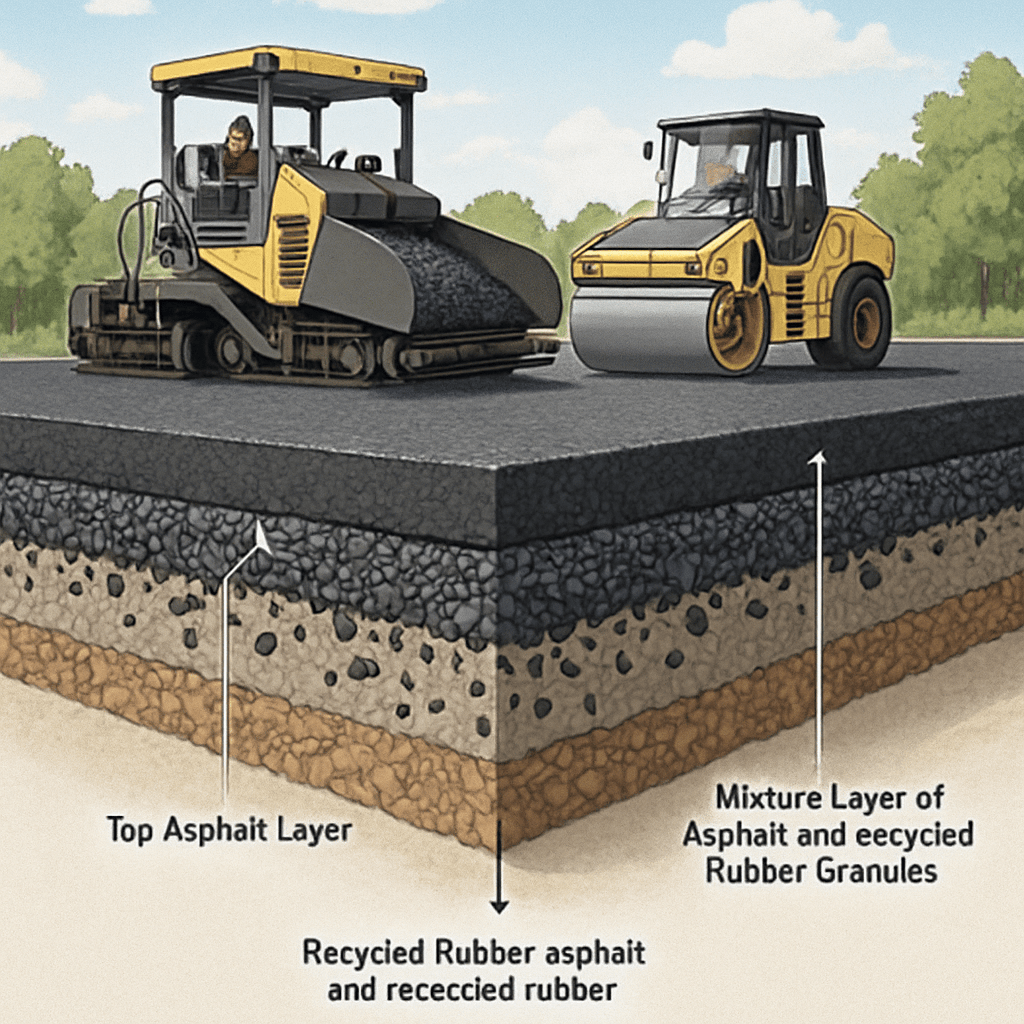
Recycled rubber—most commonly from used tires—is now actively converted into advanced road construction materials, providing both environmental and performance benefits.
How Is Recycled Rubber Used in Roads?
- Rubber Modified Asphalt: Granulated rubber from waste tires is blended into asphalt mixes, directly replacing part of traditional asphalt components.
- Process: The rubber is shredded and finely ground. It is then mixed with bitumen or asphalt (the binding agent), either at the plant or on-site, depending on the technology. Some advanced mixes also combine waste rubber with building rubble or other waste aggregates for enhanced sustainability.
- Innovative Additives: Specialty chemical companies produce process additives (such as Evonik’s Vestenamer) that improve rubber powder’s compatibility and performance in asphalt, ensuring easier mixing and better road quality.
Advantages of Rubberized Roads
- Improved Durability: Roads with recycled rubber exhibit better resistance to cracking, potholes, and rutting. Service life is extended, reducing maintenance needs.
- Environmental Impact: Each kilometer of road can recycle hundreds of old tires, preventing landfill and incineration, and giving tires a valuable second life.
- Enhanced Performance: Rubber increases road toughness and crack resistance. Properties like impermeability and noise reduction (up to 1–2 decibels) are improved, resulting in quieter and longer-lasting surfaces.
- Flexibility in Design: Engineers can optimize mixes by adjusting the rubber’s particle size and proportion (dosage), generally finding improvement in toughness and crack/frost resistance at certain levels (e.g., 15% dosage for mesh sizes 60–120).
Implementation and Trials
- Rubberized asphalt has been used successfully for decades in the U.S. and is expanding in Europe and other regions.
- Companies such as Tarmac in the UK have conducted trials on local council roads and major highways, showing excellent durability and no maintenance required years after installation.
- Innovations involving blends of rubber and building rubble have demonstrated sustainable zero-waste solutions for road-making materials.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Benefit/Detail |
|---|---|
| Material | Finely ground recycled rubber (from tires) |
| Application | Mixed into asphalt/bitumen for roads and footpaths |
| Advantages | Increased durability, reduced cracking, environmental recycling |
| Best dosage/mesh size | About 15% (for mesh sizes 60–120), depending on road specifics |
| Environmental impact | Up to 500 tires recycled per km of road |
| Additional benefits | Lower traffic noise, energy/resource savings |
This innovative use of recycled rubber in road construction is widely recognized as an advanced, sustainable solution for the future of infrastructure.
Leave a comment