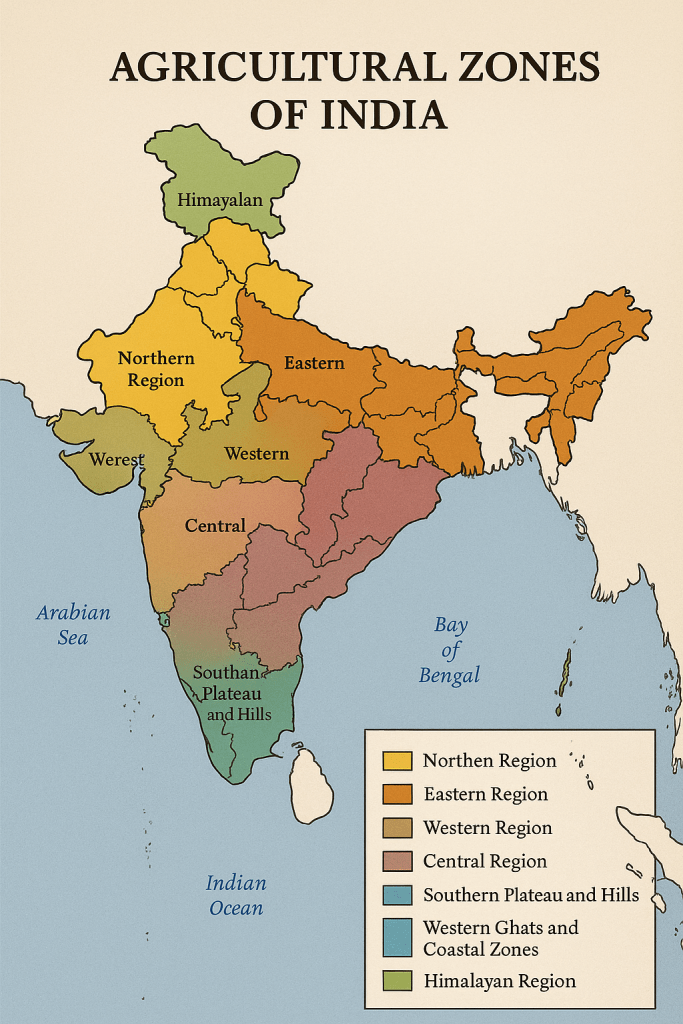
Here’s a detailed analysis of Indian states based on their agricultural zones, categorized by agro-climatic and agro-ecological conditions:
🌾 1. Northern Region (Indo-Gangetic Plains)
States: Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Delhi, parts of West Bengal
- Main crops: Wheat, rice, sugarcane, pulses, oilseeds
- Features: Fertile alluvial soil, good irrigation, dense canal system
- Challenges: Overuse of groundwater, stubble burning, monocropping (mainly wheat-rice)
🌾 2. Eastern Region
States: West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Eastern Bihar, Assam
- Main crops: Rice, jute, pulses, tea, vegetables
- Features: High rainfall, laterite/alluvial soil, suitable for paddy and horticulture
- Challenges: Floods, underutilization of resources, poor mechanization
🌾 3. Western Region
States: Rajasthan, Gujarat
- Main crops: Millets (bajra, jowar), oilseeds, cotton, pulses
- Features: Arid/semi-arid zone, sandy soil, low rainfall, drip irrigation practices
- Challenges: Drought, soil salinity, water scarcity
🌾 4. Central Region
States: Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh
- Main crops: Soybean, wheat, rice, pulses, coarse grains
- Features: Black cotton soil (regur), rainfed farming
- Challenges: Irregular rainfall, need for crop diversification
🌾 5. Southern Plateau and Hills
States: Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, parts of Maharashtra
- Main crops: Rice, ragi, pulses, oilseeds, coffee, spices
- Features: Diverse soil types (red, laterite, black), moderate to low rainfall, irrigation in river basins
- Challenges: Water scarcity, dependency on monsoon
🌾 6. Western Ghats and Coastal Zones
States: Coastal Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka coast, Kerala, Tamil Nadu coast
- Main crops: Coconut, spices, cashew, rice, arecanut, rubber
- Features: High rainfall, humid climate, lateritic soils
- Challenges: Soil erosion, cyclones, limited cultivable land
🌾 7. North-Eastern Hill Zone
States: Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Sikkim
- Main crops: Rice, maize, tea, horticultural crops (pineapple, orange, ginger)
- Features: High rainfall, hilly terrain, shifting cultivation (jhum)
- Challenges: Soil degradation, infrastructure issues, transport bottlenecks
🌾 8. Himalayan Region
States: Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand
- Main crops: Apples, walnuts, saffron, barley, maize
- Features: Temperate climate, terraced farming
- Challenges: Limited growing season, soil erosion, landslides
✅ Summary of Key Agro-Climatic Zones (as per Planning Commission):
India has 15 agro-climatic zones, such as:
- Western Himalayas
- Eastern Himalayas
- Lower Gangetic Plains
- Trans-Gangetic Plains
- Central Plateau and Hills
- Western Dry Region
- Southern Plateau
- East Coast and West Coast plains
These zones help in region-specific cropping strategies, irrigation planning, and sustainable agriculture.
Leave a comment